|
Abstract:
We report a rare case of complex fracture dislocation of
calcaneum associated with subluxation of ankle and
talonavicular joint with entrapment of FHL tendon.17 years old
gentleman who sustained the above injury due to a fall from a
height is presented .The clinical presentation , mechanism of
injury, radiological features , operative reduction and
difficulties during surgery are discussed. Post operative CT
findings and the necessity for the pre operative CT scan for the
surgical planning are emphasized.
J.Orthopaedics 2010;7(2)e13
Keywords:
Calcaneum; Dislocation; Talonavicular joint; FHL
Introduction:
Complex fracture dislocations involving the
tarsal bones are rare. Usually they are produced by high energy
injuries such as fall from a height. Bony geometry and the
strong ligamentous support between the tarsal bones confer more
stability preventing isolated mid tarsal joint dislocations with
the exception of talonavicular joint and a collective mid tarsal
joint(1).
Only a very few cases of isolated dislocation
of the calcaneum (2,3) and fracture dislocation of calcaneum
(4,6) has been reported. We are presenting this case of rare
complex injury of fracture dislocation of calcaneam associated
with subluxation of ankle, talo navicular joint and FHL
entrapment.
Case Report:
17 yrs old gentleman of
British nationality who was on a visit to Kuwait had an
accidental fall from the balcony of a house and presented to the
hospital with severe pain and swelling of the Left Ankle and
Foot.
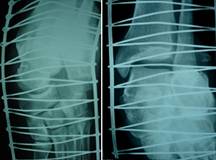
Figure 1 |
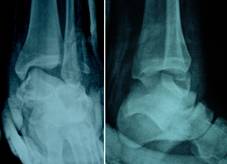
Figure2 |
He was conscious and
oriented but he could not remember how he fell down from the
balcony. On examination he had severely deformed and swollen
hind and mid foot. The skin over the medial side of the mid foot
was stretched and contused with palpable prominent navicular
head. The foot was warm with good capillary refilling of the
toes. Posterior Tibial pulse was palpable. Dorsalis pedis pulse
was felt by doppler. There was an acute fixed flexion deformity
of the big toe which could not be passively extended. There were
minor abrasions in both lower limbs and hands. . Plain Xrays of
the foot and ankle showed complete lateral dislocation of the
calcaneum from the talus and cuboid(Fig.1). The talus subluxed
and rotated from the ankle as well as from navicular bone(Fig.
2).Clinical examination and Trauma X-ray series revealed no
other musculo skeletal injuries except for the simple fracture
of the 7th rib on the Right side. C.T.Brain,Cervical Spine and
U/S abdomen were normal
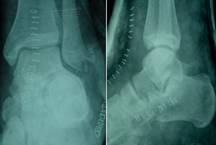
Figure 3 |
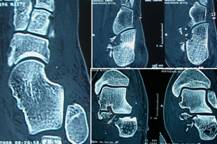
Figure 4 |
A trial of closed reduction
failed and open reduction was planned. The patient was prepared
and taken to operation theater. The Ankle joint was exposed
through Antero medial approach. The talus was reduced in to
ankle and talo navicular joint. Attempted reduction of calcaneum
in to the sub talar joint was difficult and incongruous. An
another small lateral incision was made at sinus tarsi and a
bone lever used to reduce the calcaneum through the wound. The
difficulty in reduction was due to comminuted bony fragments
involving sustentaculam tali and the entrapped FHL tendon. Small
pieces of articular fragments were removed from sub talar joint
and the wound washed. The reduction was stable. The limb was
immobilized in a well padded Below Knee plaster and kept
elevated on a Bohler frame.
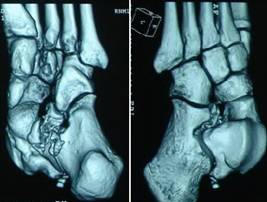
Figure 5
Post operative X-Rays
showed satisfactory reduction(Fig.3).Post operative C.T scan
(Fig.4) and the 3D reconstruction films (Fig. 5) showed the
comminuted fracture of anterior process of calcaneum involving
sustentaculam tali and the comminuted tip of lateral malleolus
which was not well recognized with plain X-Rays pre operatively.
At the time of discharge the wound was
clean.The patient was discharged with POP Cast and advised
suture removal after 3 weeks, non weight bearing for 6 weeks and
partial weight bearing for another 6 weeks. Patient has left to
his native place at UK.
Discussion :
Closed fracture dislocation involving the
calcaneum is rare. Only few cases has been reported in the
literature(4,6). However a complex fracture dislocation of the
calcaneum with subluxation of talus at ankle and navicular bone
with the entrapment of FHL tendon has not been reported.
d’Aubigue first described the case of calcaneal dislocation in
1936(5).
Court and Brown et al described the mechanism
of injury in calcaneal fracture dislocation. They postulated
that the axial loading of an inverted hind foot produces primary
sheer type fracture of the antero medial calcaneum with or
without associated postero lateral fragment. With continuation
of the force, the postero lateral fragment ruptures the lateral
collateral ligament to allow the calcaneum to dislocate(4). With
further continuation of the force the talus rotates medially on
its long axis to get subluxed from the ankle and talonavicular
joint.In our case instead of rupture of the lateral collateral
ligament, it got avulsed from the lateral malleolus with
multiple chip fracture of the tip of lateral mallelous which was
recognized in C.T scan and post reduction Xrays. Naoki Haraguchi
et al stressed the importance of special projection views to
evaluate the avulsion fractures of the lateral malleolus. Both
the anterior talofibular (ATFL) and the calcaneofibular (CFL)
ligaments arise from the anteroinferior aspect of the lateral
malleolus, and therefore avulsion fragments are superimposed on
the lateral malleolus on standard radiographs, and are difficult
to identify accurately. So, radiographs taken at 15° external
rotation with 45° of plantar flexion in projection 1, and at 45°
internal rotation in projection 2 were the most useful to asses
these injuries(7)However in patients with severe swelling and
deformity CT scan may be a better option.
Fracture dislocation of calcaneum with
tendinous interposition of FHL preventing closed reduction has
been reported by various authors(8,9). FHL originates from
distal 2/3 of posterior fibula, interosseous membrane and
adjacent intermuscular septum and its tendon passes through
posterior aspect of fibro-osseous tunnel beneath the
sustentaculum in an oblique manner, plantar midfoot (knot of
Henry); and gets inserted at the plantar surface of base of
distal phalanx of Big Toe.
Fractures involving disruption of the medial
wall at sustentaculam disrupting the integrity of the
fibro-osseous tunnel may lead to the interposition FHL at
subtalar joint causing irreducible fracture dislocation of
calcaneum(8).Fractures involving anterior extremity at
sustentaculam may be associated with calcaneocuboid
dislocation(10). Sustentaculam tali is a vital load-bearing
structure and any isolated fractures should be fixed to
prevent late hindfoot implications(11). Carr JB presented FHL
entrapment in fractures of calcaneum and described the fixed
flexed position of hallux as ‘check rein deformity’ and advised
for medial approach to release the entrapment(9).In our case we
were able to reduce the subtalar joint through lateral approach
by relocating the FHL tendon.
Conclusion:
Complex fracture dislocation of calcaneum
with FHL entrapment at subtalar joint causing difficulty in
reduction at subtalar joint has been presented. The importance
to have a pre operative C.T scan if available for the
evaluation of the injury pattern, planning the surgical approach
and fixation if needed has been stressed.
Reference :
-
Piney SJ, Sangeorzan BJ.
Fractures of the tarsal bones. Orthop Clin North Am
2001;32:21-32.
- Viswanath SS, Shepard E. Dislocation of the calcanium.
Injury 1977; 9:50.
- Rao H. A complete dislocation of the calcaneus: a case
report. J Foot Ankle Surg 2005;44(5):401-5.
- Court-Brown CM, Boot DA, Kellam JF. Fracture dislocation
of the calcanius. Clin Orthop 1986;213:201-6.
- d’Aubigue MR. Fracture isolee de la petite apophyse du
cal-caneum traitee par osteosynthese (Raport de M. Wilmoth).
Mem Acad Chir 1936;62:1155.
-
Julian R. Northover, Stephen A.
Milner: Fracture dislocation of the calcaneum: a case report.
Injury Extra2006;37:294-296.
-
Haraguchi N, Kato F, Hayashi H. :
New radiographic projections for avulsion fractures of the
lateral malleolus.
J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80(4):684-8.
-
Anglen JO,
Gehrke J.:Irreducible
fracture of the calcaneus due to flexor hallucis longus tendon
interposition.
J Orthop Trauma.
1996;10(4):285-8.
-
Carr JB: Complications of
calcaneus fractures: Entrapment of the flexor hallucis longus.
Report of two cases. J Orthop Trauma 1990;4:166-168.
-
Hagino T,
Tonotsuka H,
Ochiai S,
Hamada Y: Fracture of the
anterior extremity of calcaneus together with calcaneocuboid
joint dislocation.
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009
;129(12):1673-6.
|







