|
Chintan Rohitkumar
Bhatt, Meenakshi Sanjay Modi, Chandrakant D Mehta
Govt Medical College, Surat.
Address for Correspondence:
Chintan Rohitkumar
Bhatt
Tutor in Anatomy
Govt Medical College, Surat,India.
E-Mail: drchintanbhatt@yahoo.co.in
|
|
Abstract:
Peroneus tertius (PT) is a muscle of the anterior compartment of
the leg. The PT muscle originates from the anterior surface of
the fibula and the interosseous membrane and inserts into the
medial side of the dorsal region of the fifth metatarsal bone.
We have dissected 94 cadavers to see the variation in the
Peroneus tertius muscle, we found some or the other variation in
8 cases, and absence of muscle in 10 cases. In the variation the
common variation is that the PT tendon arises from the tendon
the fourth digitations of the extensor digitorium longus or just
an extension of it. Usually, the PT is involved in dorsiflexion
and eversion of the foot. In many cases, the absence of PT maybe
asymptomatic and it may be incidentally detected during
cadaveric dissections or autopsies. The existence of PT may help
in the swing phase of bipedal walking. The PT may be used for
tendon graft surgeries. The pull of the PT may be responsible
for causing stress on the fifth metacarpal and account for all
stress fractures in any individual. The absence of the PT may
puzzle any transplant and foot surgeons performing graft
operations. We as anatomists discuss the clinical implications
of the variations of PT.
J.Orthopaedics 2010;7(2)e1
Keywords:
Peroneus tertius muscle; variation; dissection.
Introduction:
Peroneus tertius (PT) is a muscle of the anterior compartment of
the leg. The PT muscle originates from the anterior surface of
the fibula and the interosseous membrane and inserts into the
medial side of the dorsal region of the fifth metatarsal bone.
With the adaptation to erect posture the foot had not only to
bear weight but also to maintain the balance of body while
walking and standing on uneven surfaces. The Peroneus are the
cornerstone muscles that have evolved to perform this function
muscles Variations of these
are more frequent than supposed and their distal attachments are
not absolutely at a fixed position. The Peroneus muscles may
show variations as a whole or share in a certain measure the
general prerogatives of the muscular system. These muscles
attract attention on account of their pronounced relation to the
plantar or tarsian arches. They are major everters and are
involved in complex actions such as dancing and skating. The
importance of the role of Peroneus in the pathogenesis of pes
cavovarus may be more crucial than has been reported.
Materials
and Methods:
We have observed 94 cadaveric lower limbs which are given to the
undergraduate students to dissect in the government medical
college, Surat and from the municipal medical college, Surat for
last 3 years. The dissection was done by the students under
guidance of the teachers and according to the Cunningham manual
of dissection of anatomy.
The Peroneus tertius muscle is the muscle of anterior
compartment of the leg. We have studied 94 cases for the
variation in the Peroneus muscle. We have found that in 10 cases
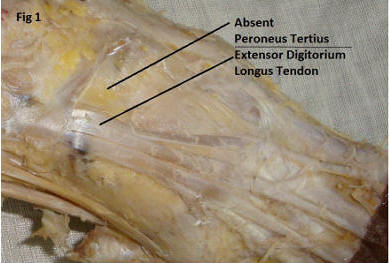
Peroneus tertius muscle is absent. As we can see in the fig.1
that the Peroneus tertius muscle is absent in this case.
The other common variation of the Peroneus tertius muscle that
slips arises from the 4th tendon of extensor
digitorium longus. This slip strengthens the muscle and helps in
the action of PT.
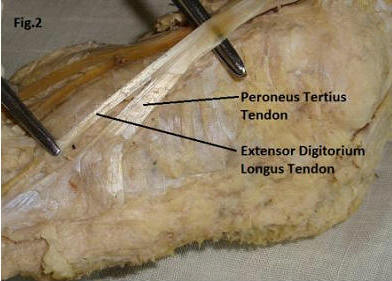
In other case as we can seen in the fig that one extra slip of
fibers are going from the extensor digitorium longus to the
Peroneus tertius. Such types of 6 cases have been found.
(Fig.2).
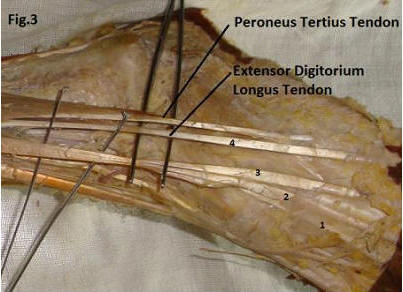
As we can see in fig.3 in 2 cases we found that the Peroneus
tertius muscle and the fourth digitations of the extensor
digitorium
longus has a single belly where as their insertion is at their
normal anatomical site.
Discussion :
The peroneus tertius is absent in 5% to 17% of the human white
population. The function of the peroneus tertius is eversion and
dorsiflexion of the foot. These 2 strength parameters have been
identified as important parameters in the development of ankle
ligament injuries.1 The study by Das SS shows that
absent of Peroneus tertius muscle is around 10.5% of Cases.2
We found 10 cases of absence Peroneus tertius muscle. This
figure is almost similar with other authers such as Wood
(9.8%),Le Double (9.1%), J Bertelli & Z Khoury(9.1%).3
Peroneus tertius muscle is helpful in the swing phase of the
bipedal mode of locomotion. The tendon of Peroneus tertius
muscle also helpful in the transplant surgeries. We also found
the 6 cases where the Peroneus tertius muscle is just the extra
digitations or slips of fibers arises from the 4th
tendon of the extensor digitorium longus muscle. The maximum
length of the slip is 7.2 cm and the mean length is 6.4cm. The
insertion of the both muscle is at the usual site. The slip
generally arises after the tendon crosses the ankle joint. It
shows that the muscle has limited role in dorsiflexion at the
ankle joint. The clinical importance of the Peroneus tertius
concerning prevention and treatment of ankle ligament injuries
is low.1 In the two case it has been shown that the
Peroneus tertius and the fourth digitations of extensor
digitorium longus has a single belly and both muscle splits at
the higher level than usual. Such type of muscular variation is
not noticed yet and such variation helps in prevention of ankle
ligament injury. The pull of the PT may be responsible for
causing stress on the fifth metacarpal and account for all
stress fractures in any individual.4
The presence of an anomalous m. Peroneus
tertius tendon has also been described to be associated with a
m. peroneus brevis tear. (5, 6) Peroneus brevis tear
is one of the important cause of the chronic ankle pain.7
Conclusion:
Our human data indicate that during bipedalism peroneus tertius
functions in concert with extensor digitorum longus and tibialis
anterior as a swing-phase muscle in order to level the foot and
help the toes clear the ground. The lack of support-phase
activity in peroneus tertius contradicts suggestions that it
acts primarily to support the lateral longitudinal arch and/or
to transfer the foot's center of pressure medially while the
font is in contact with the substrate. Lacking a peroneus
tertius, our nonhuman subjects frequently recruited peroneus
longus and peroneus brevis (plantar flexor/evertors) during
swing phase. The acquisition of peroneus tertius in the hominid
lineage has endowed us with a mechanically advantageous
dorsiflexor/evertor that presumably improves the economy of
human bipedalism.
Reference :
-
Witvrouw E, Borre
KV, Willems
TM, Huysmans
J, Broos
E, De
Clercq D:The
significance of Peroneus tertius muscle in ankle injuries: a
prospective study: Department of Rehabilitation Sciences and
Physical Therapy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences,
Ghent University, Belgium.
erik.witvrouw@ugent.be
-
Joshi SD, Joshi SS Athavale SA: Morphology of Peroneus Tertius
muscle: Department of anatomy,Rural Medical College, Loni,
Ahmednagar, India.
-
J Bertelli & Z Khoury:The Peroneus tertius island muscle flap:
Journal of clinical anatomy;Sur. Clinical anat (1991)
13:243-244
-
Das S, Haji Suhaimi F, Abd Latiff A, Pa Pa Hiaing K, Abd
Ghafar N, Othman F: Absence of the Peroneus tertius muscle:
cadaveric study with clinical considerations: Dept. of
anatomy, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kurala Lumpur,
Malaysia,
faizah@medic.ukm.my.
-
Sobel M, Bohne WH, Levy ME. Longitudinal attrition of the
peroneus brevis tendon in the fibular groove: an anatomic
study. Foot Ankle 1990;11:124-8.
-
Sobel M, Mizel M. Injuries to the peroneal tendons. In:
Pfeifer GB, Frey CC, editors. Current practice in foot and
ankle surgery. Vol 1. New York: McGraw Hill; 1993. p. 30-6.
-
Sobel M, Geppert MJ, Olson EJ, Bohne WH, Arnoczky SP. The
dynamics of peroneus brevis tendon splits: a proposed
mechanism, technique of diagnosis, and classification of
injury. Foot Ankle 1992;13:413-22.
|





