|
Abstract
A retrospective and prospective study was
carried out from Jan 2001 to Dec 2005 to study results of
treatment of Neer’s four part fracture proximal humerus using
different modalities of treatment. In our study 30 cases were
selected with age group ranging from 20 yrs. to 90 yrs. 26 were
male patients. The follow up length was average 2 years with
range from 18 months to 3 yrs. Each patient was treated with one
of the following procedures: closed reduction and arm chest
strapping, closed reduction & percutaneous k wire fixation ,
open reduction & internal fixation with plate or
hemiarthroplasty. Patients were evaluated with Neer’s scoring
system at specific intervals. Overall 73 % of patients showed
satisfactory to excellent results. Satisfactory to excellent
results were noted in 7 out of 8 patients treated with open
reduction and internal fixation with plate, while 5 out 7 for
percutaneous k wire fixation and 2 out of 6 for closed reduction
and arm chest strapping. All 8 patients undergone
hemiarthroplasty showed satisfactory to excellent results. We
conclude that appropriate selection of the modality of treatment
depending on age, bone quality & comminution etc. gives good
results.
Key words: Four part fracture proximal humerus, Arm-chest
strapping, Open reduction, Internal fixation, Percutaneous
k-wire, Hemiarthroplasty.
J.Orthopaedics 2006;3(4)e9
Introduction:
Fractures of the proximal humerus was
initially considered to be geriatric injury. It is now
increasingly seen in young people with good bone stock and
predominantly male patients are seen. There were relatively few
reports of treatment of the more complex fractures until Neer’s
report emphasized the need to be more aggressive with what he
described as three and four-part fractures of the proximal part
of the humerus
Many authors advise that prosthetic
replacement for four-part fractures should be reserved for
elderly patients with osteoporosis and patients with irreparable
fracture-dislocations. While others reported variable results
after using osteosynthesis , percutaneous k wire fixation & arm
chest strapping for treatment of four-part fractures.
Aim of this study was to evaluate results of
different modalities to treat four part fracture of proximal
humerus.
Material and Methods :
Retrospective and prospective study was
carried out from Jan 2001 to Jan 2005 for evaluation of
different modalities to treat Neer’s four part fracture of
proximal humerus. In our study 30 cases were selected. 26 were
male patients. Age group was from minimum 20 to maximum 90 yrs
of age. The length of follow up was average 2 years with range
from 18 months to 3 yrs. Anteroposterior, lateral scapular or
axillary radiographs were taken. Fractures of proximal end
humerus with X ray showing 4 part fracture with displacement >1
cm or 45degrees were selected.5,1 Initial temporary treatment
was given in the form of sling support and arm chest strapping.
All patients were treated by one of the
following options
-
Closed reduction and nonoperative treatment
–immobilization with arm to chest strapping
-
Closed reduction and percutaneous k wire
fixation
-
Open reduction and internal fixation with
clover leaf plate,
-
Hemiarthroplasty
Modality of the treatment was selected on
following guidelines:
-
elder age group >60yrs.
-
without dislocation with better alignment.
-
unfit for surgery-medical problem.
-
patient not willing for the surgery.
-
young individuals.
-
closed reduction possible.
-
good bone quality.
-
young individuals < 60 or physiologically
active.
-
with dislocation.
-
closed reduction not possible.
-
good bone quality.
-
elder age group > 60.
-
osteoporotic bones.
-
with dislocation.
-
with comminution.
Approach used for surgery was deltopectoral.
Implants used were cloverleaf plate, 4mm cancelloue screws,
4.5mm, 3.5mm cortical screws Neer’s prosthesis. For K wire
fixation 3-4 wires were used. Patients who
needed surgery were posted for the surgery at the earliest.
Postoperative protocol:
1. The extremity was placed in an arm chest
strapping for 3 weeks. If secure fixation was achieved, gentle
pendulum exercises were begun. Careful judgment is required
here. If the bone is severely osteoporotic and fixation is less
than rigid, motion was delayed.
2. Pendulum exercises were permitted by the
second or third week when the fragments are rigidly fixed,
3. Gentle passive forward flexion and
internal and external rotation exercises were permitted by the
third or fourth week.
4. After e 4 to 6 weeks active or resistive
exercises were permitted.
Then patient was asked to follow up at 3
weeks , 6 weeks, 3 months and 6 months and then 6 monthly. 10
old follow-up patients were also evaluated retrospectively after
variable periods .The average stay of the these patients after
the surgery was 10 days.
At each follow up following points were taken
into consideration. 1.pain 2. function 3.range of motion
4.anatomy. These criteria are proposed by Neer. The maximum
points- 100 units.
Pain - 35 units
Function - 30 units
Range of movement - 25 units
Anatomy - 10 units
On overall scores the patients were grouped
into
Excellent- >89 units
Satisfactory- 80-89 units
Unsatisfactory- 70-79 units
Failure- < 70 units
Results :
1. Age
distribution:
|
Age Group in years |
No. of Patients |
|
20 – 40 |
9 |
|
40 – 50 |
8 |
|
50 – 60 |
5 |
|
> 60 |
8 |
Out of 30 patients 9 were from age group
20 – 40 yrs, while 13 patients were > 50 yrs, rest were in age
group 40 –50.
2. Mechanism of injury:
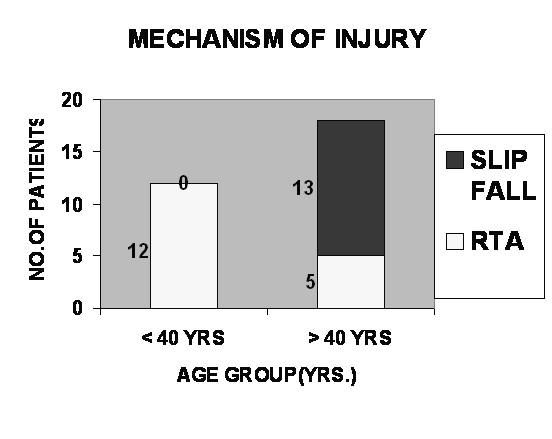
Out of 30 patients 13
patients had mechanism of injury as fall on outstretched hand.
Other 17 patients had road traffic accident and direct injury to
shoulder. All patients having history of fall on outstretched
hand were > 40 yrs. In 17 patients of direct injury 12 were of
age group 20-40 yrs. And remaining were 40-50 yrs.
3. Male to Female ratio
Out of 30 cases , 4 were female patients.
4. Modality of treatment offered:
|
MODALITY OF TREATMENT
|
NO.OF PATIENTS |
|
Closed reduction+AC Strapping
|
6
|
|
Closed reduction+ P/C
Kwire
|
7
|
|
Open reduction & internal fixation
|
9 |
|
Hemiarthroplasty
|
8 |
|
Total |
30
|
5. Age group wise selection of modality
of treatment:
|
AGE GROUP(YRS.)
|
CR + AC STRAPPING
No. of Patients
|
O RIF
No. of Patients
|
CR+ P/C K WIRE
No. of Patients |
HEMIARTHROPLASTY
No. of Patients |
|
20 – 40
|
1 |
8 |
0 |
0 |
|
40 – 50
|
0 |
1 |
4 |
1 |
|
50 – 60
|
1 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
|
>60
|
4 |
0 |
1 |
5 |
|
TOTAL
|
6 |
9 |
7 |
8 |
6. Results of each procedure according
to Neer’s criteria:
a. Closed reduction & arm chest strapping:
Out of 30 patients 6 patients were treated
with CR & AC strapping. Out of which 5 patients were above
50 yrs. Age. 1 patient who was was trearted with Ac strapping
was 30 yrs old and was a case of rheumatic heart disease –unfit
for surgery.
|
NEER’S SCORING
|
CR+AC STRAP.NO. OF PTS. |
|
EXCELLENT
|
0 |
|
SATISFACTORY
|
2 |
|
UNSATISFACTORY
|
3 |
|
FAILURE |
1 |
2 patients showed satisfactory results
while 4 patients showed unsatisfactory results.All patients who
showed unsatisfactory results had painful and stiff shoulder .
b. Open reduction & internal fixation:
9 patients were treated with ORIF , out of
which 8 were in age group of 20 to 40 yrs.
|
NEER’S SCORING
|
ORIF (NO. OF PATIENTS) |
|
EXCELLENT
|
2 |
|
SATISFACTORY
|
5 |
|
UNSATISFACTORY
|
2 |
|
FAILURE
|
0 |
7 of patients showed
satisfactory to excellent outcome while 2 showed unsatisfactory
outcome. Implants used was Cloverleaf plate. One patient had
plate and screw loosening while one patient developed AVN and
delayed posttraumatic arthritis. One patient had painful
shoulder due to migration of screw intrarticularly which was
removed later .Patient was painfree after that.
c. Closed reduction & percutaneous Kwire:
7 out 30 patients were treated with CR
followed by percutaneous k wire fixation. All were in the age
group of 40 to 60 years.
|
NEER’S SCORING
|
CR +K WIRE(NO. OF PATIENTS) |
|
EXCELLENT
|
2 |
|
SATISFACTORY
|
3 |
|
UNSATISFACTORY
|
1 |
|
FAILURE
|
1 |
5 patients showed satisfactory to
excellent outcome and 2 showed unsatisfactory to poor outcome.
One patient showed inferior subluxation of head in follow up
visit.
d. Hemiarthroplasty:
5 cases were more than 60 yrs. All patients
were severely osteoporotic with comminution and elderly age
group except one.
|
NEER’S SCORING
|
HEMIARTHROPLASTY (NO. OF PTS.) |
|
EXCELLENT
|
6 |
|
SATISFACTORY
|
2 |
|
UNSATISFACTORY
|
0 |
|
FAILURE
|
0 |
6 patients
showed excellent outcome and 2 patient showed satisfactory
outcome.
7. Overall Outcome of the patients in our study:
|
UNITS |
NO. OF CASES |
RESULT |
PERCENTAGE |
|
Ø 90
|
10 |
EXCELLENT |
33 |
|
80 – 89 |
12
|
SATISFACTORY |
40 |
|
70 – 79 |
6
|
UNSATISFACTORY |
20 |
|
60 – 69 |
2
|
FAILURE |
7 |
|
TOTAL 100 UNITS |
|
|
|
Overall 70% of patients showed satisfactory
to excellent outcome
COMPLICATIONS:
|
COMPLICATION |
NO. OF CASES |
|
1. MALUNION
|
8 |
|
1. PIN TRACT INFECTION
|
2 |
|
2. MIGRATION OF SCREWS INTO THE JOINT
|
1 |
|
4. PLATE & SCREW LOOSENING
|
1 |
|
5.WOUND HEALING
|
1 |
|
6. DELAYED ARTHRITIS & AVN
|
1 |
|
7.POST OPERATIVE INFERIOR SUBLUXATION
|
1 |
Discussion :
Fractures of the proximal humerus are seen in all age groups,
now increasingly seen in younger age group with good bone stock
and predominantly male patients are seen. Selection of modality
of treatment of four part fracture as per the indications
already mentioned gives good results. Adequate preoperative
planning and necessary equipment for the fixation has to be
ensured.
In decision making of selection of modality of treatment,
following factors are found to play important role:
Fracture factors:
1. Degree of displacement, 2.Comminution,3. Bone
quality,4. Articular surface involvement
Patient factors:
1. Functional needs,2.Preexisting
disabilities,3.Age,4.Ability to participate in the
rehabilitation programme
Technique of closed reduction and arm chest strapping was
opted in the elderly patients who did not have high functional
demands, unfit for surgery, were not ready for the surgery .
These patients were cases of 4 part fracture without
dislocation. In 1 case there was fracture dislocation but we
could reduce the head fragment by closed reduction under short
GA. We could achieve satisfactory results in only 2 . Out of 5
patients 3 patients had restricted abduction ( up to 90degrees)
, flexion and internal rotation and painful shoulder on further
movement. But because of their sedentary life style & less
demands they could carry out day to day household work. Few series like Leyshon (Acta orth Scand 1984), Stableforth (JBJS
1984), Svend Hansen (Acta orth Scand 1974) report satisfactory
result upto 5 %.3,7. Few other series report satisfactory results. 9
We found that while dealing with fixation of displaced or
irreducible proximal humeral fractures open reduction and
internal fixation appears to provide secure fixation and
rotational control of the fracture complex with minimal hardware
and risk of soft tissue impingement. We opted for open reduction
and internal fixation in 9 out of 30 patients who all were
young age group patients(20-40yrs) with good bone stock, and
high demands in the form of strong functional shoulder. 3
patients had fracture dislocation which was reduced first
intraoperatively. Position of the plate should not be too high . We could achieve satisfactory to excellent results in 7 out
of 9 patients. A. J. Wijgman, MD, W. Roolker (JBJS 2002) have shown in
their series of ten years of follow-up 87% had a good or
excellent result on the basis of the Constant score when treated
with open reduction and plating 8. Pavolainen et al.(Acta Orth Scand 1983) 6 and Dr. S.K. Moda
have also shown similar results (JBJS 1990) 4.
Advatages of ORIF were:
- It was useful for severly displaced as well as dislocated 4
part fractures
- Less pain with early physiotherapy.
Disadvantages were:
- wider exposure,
- high chances of AVN,
- subacromial impingement,
- implant related complications,
- nerve lesions.
The technique of closed reduction and percutaneous pinning is
quite demanding technically .It may appear deceptively simple .
This technique makes sense , biologically, from standpoint of
retention of vascularity. It is useful alternative to open
reduction and internal fixation for displaced fractures of
proximal humerus that can be reduced but unstable. We treated 7 patients with closed reduction and percutaneous
pins. Age group was 40 –60yrs. 5 of patients showed satisfactory to
excellent results & 2 showed unsatisfactory to poor results.
Jakob, Jaeberg & Warner 1984 series of same modality of
treatment showed 70 % good or excellent results.2
We found that while dealing with 4 part fracture in elderly
age groups with osteoporotic bone ,prosthetic replacement
provided good results. We performed hemiarthroplasty in 8
cases. 5 patients were > 60 yrs. Outcome was excellent in 6 and
satisfactory in 2 of patients. Pain relief was good and fair
function was possible. Choice of closed reduction/open reduction and internal
fixation versus Hemiarthroplasty was a multifactorial decision.
We believe that the success of the operation depends not only on
the prosthesis but also other several well defined factors .
These include proper operative techique based on principles of
restoration of humeral length , anatomical fixation of
tuberosities with ultimate healing to the shaft and appropriate
degree of retroversion. Nonunion and nonanatomical position of
tuberosities definitely affects the outcome. Different series world wide show variable outcome 20-90%
satisfactory results. Fischer , Nicholson, Mcllveen 1992 showed 86% satisfactory
results.(> 90 degrees elevation and pain free) & Neer Mcllveen
(Chir. orthop. Suppl. 1988) showed 85 % satisfactory results.
9,10
We had our share of the complications. We had malunion
problem in 8 patients. Pin tract infection, wound healing
problem could be taken care of and did not affect the outcome.
Screw purchase in osteoporotic bone was poor sometimes leading
to early loosening and migration. Appropriate length of the
screws is must which can be confirmed under image intensifier to
avoid complication of migration of screw in the joint.
Conclusion:
Our study brought out following
findings which need further study and analysis.
Most of the
four part upper end humeral fractures > 40 yrs. are primarily related
to osteoporosis and caused due to slip and fall on outstretched hand
i.e. indirect injury .
Nowadays
increasing number of 4 part fractures seen in young age group
with good bone stock predominantly in males due to increase in
the high velocity road traffic accidents i. e. direct injury.
In four part
fractures in young age group (20-40yrs.) which are irreducible
, with good bone stock and high demands in the form of strong
functional shoulder –open reduction and internal fixation gives
good results.
In a
very old patient with less functional demands and who is unfit
for surgery or not willing for surgery, closed reduction and arm
chest strapping remains a viable option with the patient
accepting restricted range of movement and pain.
Closed
reduction and percutaneous pinning is a useful alternative to
open reduction and internal fixation for displaced four part
fracture that can be reduced but unstable. Though technique
appears simple is highly demanding, technically and biologically
very good.
In elderly
patients with osteoporotic bones with comminution with limited
functional demands hemiarthroplasty is the treatment of the
choice.
Satisfactory outcome of the treatment is equally dependent on
reduction –fixation as well as effective postoperative
rehabilitation.
Reference :
-
Jakob, R.P.,
Miniaci, A., Anson, P.S., Jaberg, H., Osterwalder, A., and
Ganz, R.: Four-part valgus impacted fractures of the proximal
humerus. J. Bone Joint Surg., 73B:295–298, 1991.
-
Jaberg, H.,
Warner, J.J., and Jakob, R.P.: Percutaneous stabilization of
unstable fractures of the humerus. J. Bone Joint Surg.
74A:508–515, 1992.
-
Leyshon,
R.L.: Closed Treatment of Fractures of the Proximal Humerus.
Acta Orthop. Scand. 55:48–51, 1984.
-
Moda open
reduction and internal fixation of proximal humerus JBJS
1990-72b,1050-2
-
Neer, C.S.:
Four-Segment Classification of Displaced Proximal Humeral
Fracture, C.S.: Prosthetic Replacement of the Humeral Head:
Indications and Operative Technique. Surg. Clin. North Am.,
43:1581–1597, 1983.
-
Paavolainen,
P., Bjorkenheim, J.-M., Slatis, P., and Paukku, P.: Operative
Treatment of Severe Proximal Humeral Fractures. Acta Orthop.
Scand., 54:374–379, 1983
-
Stableforth,
P.G.: Four-Part Fractures of the Neck of the Humerus. J. Bone
Joint Surg., 66B:104–108, 1984.
-
Wijgman
A.J.,MD,W.Roolker open reduction and internal fixation of
three & four part fractures proximal humerus.JBJS 2002
-
Rockwood
and Green’s Fractures in adults edition IV
-
Campbell
Operative Orthopaedics , Edition 9
|



