Address for Correspondence:
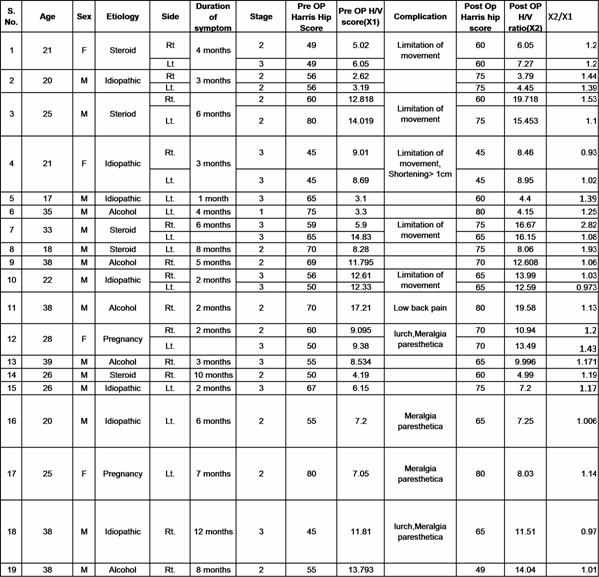
Dr Rajat Malot
693, luv kush marg, vivek vihar
New sanaganer road Jaipur, 302019
phone :9460326673
Email :rajatmalot@gmail.com
Abstract:
Background : Avascular necrosis of the adult hip remains one of the more challenging problems facing the orthopedic surgeon. It affects primarily young adults and is bilateral in more than 60% of individuals.The results of Head preserving surgeries are better than Arthroplasty .The purpose of the study is to determine the diagnostic efficacy of SPECT ( bone scintigraphy) in AVN of the femoral head and to evaluate the results of iliac crest muscle pedicle graft and core decompression in avascular necrosis of head of femur by quantitative follow up SPECT.
Material and Method: In this series 19 cases (26 hips) of non traumatic avascular necrosis head of femur Stage 2 and Stage 3 of Ficat and Arlet have been studied. The average age in series was 30.84 years .Alcohol and Steroid were leading causes. Average duration between onset of symptoms and operation was 4.95 months. Patients were operated and Tensor fascia lata grafting done. A H/V ( Head upon Vertebra) ratio on third phase (skeletal image) is taken pre operatively and compared with post operative H/V ratio at 6 month. When pre and post H/V ratio had markedly increased (greater than 1.2) then the disease was in progression stage and the procedure was not successful. When the H/V ratio was normal, decreased or slightly increased then disease was in static phase or the pathology of the disease had been halted.
Results: In present series on comparing bone scan, among 26 hips, 5 hips showed marked increase in H/V ratio thereby showing development of secondary arthritis. 19 hips showed either normal or slight increase in the ratio or 2 hips showed slight decrease in the H/V ratio. Pain was relieved in all the cases
Conclusion : Muscle pedicle bone graft is a very good treatment modality especially in early stage of the disease and bone scan is a good tool to know the disease progression and effectiveness of any treatment modality used.
J.Orthopaedics 2011;8(4)e9
Keywords:
Core decompression; Muscle pedicle graft; Bone Scan
Introduction:
Avascular necrosis of the adult hip remains one of the more challenging problems facing the orthopedic surgeon. It affects primarily young adults and is bilateral in more than 60% of individuals. It is being diagnosed with increasing frequency.
Without definitive treatment, 70% to 80% of clinically diagnosed cases will progress and most will require some form of arthroplasty.
It is generally agreed that successful treatment of patients with AVN is directly related to the stage at the time of diagnosis. The goal of treatment of osteonecrosis of head of femur is preservation of head in early stages of disease by various hip preserving methods and to delay arthroplasty.
Tensor fascia lata graft is a very effective head preserving procedure in early stage of the disease and its advantages are:
1.It has high quality of iliac crest spongiosa.
2.The necrotic/poorly vascularised bone is removed and replaced with autogenous bony material with reliable blood supply.
3.Lack of need of vessels anastomosis.
4.Temporary delay/prevention of secondary deformity of femoral head.
Diagnosis of AVN is made on the basis of clinical examination, radiographic changes, MRI, and Bone scan. Advantage of bone scan is that the counts emitted before and after the surgical intervention can be compared and reliable conclusion can be made.
Materials and Methods
26 hips in 19 patients were included in the study from December 2007 to October 2009. The Inclusion criteria for patients in this series were: Non traumatic AVN Ficat and Arlet Stage 2 (14 hips) and Stage 3(12 hips),age between 19 to 50 year,bone scan showing AVN changes. The average age in series was 30.84 years.Out of 19 cases, 15(79%) were male and 4(21%) were female. Male female ratio was 3.75: 1. Disease was bilateral in 7 patients. Among Non Traumatic causes, Alcohol and Steroid were leading causes. There were 5 patients (26%) of each cause. In 7 patients (37%) no causes was identified and were labeled Idiopathic. In 2 female patients (11%), the cause of AVN was Pregnancy in which altered hormonal balance seems to be the etiology. Average duration between onset of symptoms and operation was 4.95 months.TFL muscle pedicle grafting performed.
The Harris hip score reflecting pain, walking function, activities of daily living,and range of motion (ROM) of hip,was assessed preoperatively and at last follow up.
Pre Operative H/V ratio and Post Operative H/V ratio at 6 month is calculated at three phase bone scan.Disease was graded as progressed, improved or deteriorated on comparing H/V ratio.
Technique of tensor fascia lata muscle-pedicle bone graft
With the patient in the supine position and a small sandbag behind the buttock of the affected side, an incision is made from a point about 7.5 cm behind the anterior superior iliac spine, along the outer lip of the iliac crest.
The groove between sartorius and TFL is identified and the deep fascia overlying TFL is raised. An incision is then made in the muscle fibres of the TFL, in their direction, 2.5 cm behind the anterior edge of the muscle.
The isolated anterior fibres of TFL are elevated and its deeper fibres, found intermingled with those of the underlying gluteus minimus, are sectioned. A segment of the iliac crest 2.5 cm long and 2.5 cm broad is osteotomised and retracted down, keeping its attachment to the anterior fibres of the TFL intact.
The exposed gluteus minimus muscle is erased from the outer surface of the ilium and retracted down, and the straight and reflected heads of rectus femoris are retracted. Next, the anterior capsule of the hip is opened, using an inverted T-shaped incision.
A window was made around 3cm in width and length unicortical on the anterior surface of the neck. A stab incision was given on the lateral side of thigh at the level of the greater trochanter and through it a 4.5mm drill was passed into the head at the side of the necrosis and multiple drilling of the head was done thereby relieving congestion. Bone marrow taken from iliac crest was put in the necrotic region of head through the neck.
The TFL graft was rerouted and fixed to the window made in the neck provisionally with a 1.8mm K wire. Drilling with 2.5mm drill bit done on the placed graft, size measured and appropriate 3.5mm cancellous screw was put to fix the graft to the neck. The cut margins of the capsule were then repaired to secure the graft.
Physiotherapy in form of suspension sling exercises, static quadriceps exercises were encouraged early in the postoperative period. Hip flexion and Active straight leg exercises movements were started at four weeks with the patient still in bed. Crutch walking, non-weight-bearing on the affected leg was allowed from six to eight weeks.
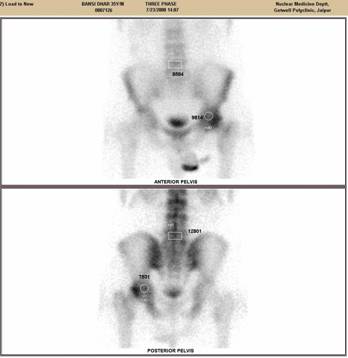
Bone scan findings: A region of interest (ROI) was drawn containing that AVN Head in anterior as well as posterior images. A similar ROI was drawn on the vertebrae L5. The number of pixels enclosed in respective ROIs was kept constant during the successive follow up studies in each patient. Counts emitted from each ROI were a measure of the amount of tracer delivered to the enclosed region.
For every patient, H/V ratio was calculated on the third phase image of the bone scan done pre-operatively and on the follow up scan at 6 and 1 year.
H/V ( Pre Op) = H(ant.) +H(post)
V(ant.) +V(post)
Results :
The Harris score increased (p<0.001) from a mean of 50 points preoperatively to 76 points at last follow up. All patients had preoperative pain, and pain is relieved in every case of AVN irrespective of the stage at which it is performed. Postoperative on final follow up 8 (31%) hips had improved from radiological stage 3, 2 and 1 to 2, 1 and normal respectively (43%) hips remained unchanged and 7 (26%) hips got deteriorated to advanced stages.
In current series, 18 hips(70%) had X2/X1 ratio in between 1 and 1.2 showing increase in vascularity of femoral head after muscle pedicle graft while in 5 hips(20%), X2/X1 ratio was >1.2 showing increase of the disease process despite muscle pedicle graft ,probably due to collapse of head and secondarily degenerative arthritis of hip joint.
The most common complication after muscle pedicle bone graft was restriction of hip movement in 10 hips (38.5%). In these, flexion, abduction and internal rotation movement were most commonly involved. Four hips (15.4%) developed meralgia paresthetica due to intra operative damage to lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. One patient developed significant shortening due to collapse of femoral head. None of the patient in this series had infection or fracture neck of the femur
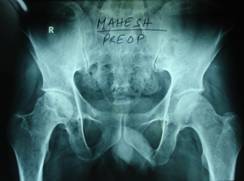
X ray of pelvis showing AVN of right hip
Figure-1 (a)
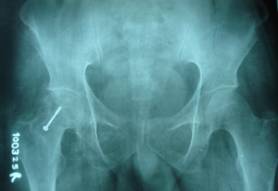
x ray at 1 year follow up after doing muscle pedicle bone grafting showing arrest of the disease
Figure-1 (b)
.
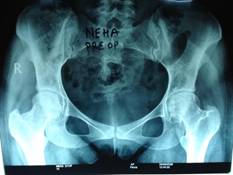
21 years girl having AVN bilateral hip after taking steroids for skin disease
Figure-2 (a)
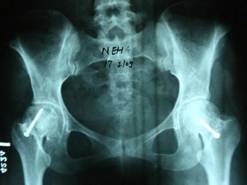
Post operative radiograph at 6 months ,bilateral TFL muscle pedicle graft done
Figure-2 (b)
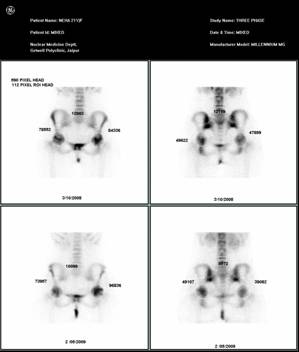
Bone scan of the patient : upper half showing pre operative count and lower half showing post operative count. the H/V ratio postop to pre op is less than 1.2 thereby showing that disease process is halted
Figure-2 (c)
.
DISCUSSION:
Muscle pedicle bone graft appears to be a good option in patients of AVN in pre collapse stage as the results of arthroplasty in young patients with AVN are not good.Baksi reported good relief in pain in all patients of AVN .we also head almost complete relief of pain in almost all patients.
The Harris Hip score improved post operatively in MPBG group from 50 to 76. There was statistically significant improvement in the Harris hip score thereby proving the beneficial result of muscle pedicle graft.Radiologically staging preoperative 2 hips were stage 1, 12 hips stage 2, 12 hips stage 3. Postoperatively 8 hips improved, 11 hips unchanged and 6 hips deteriorated.
Radiologically collapsed, flattened head and reduced joint space, changes did not improve and remained static or deteriorated to advanced stage.
In 1997 Sedonja I, Jevtic V, Milcinski Mpublished article” Bone scintigraphy as a prognostic indicator for bone collapse in the early phases of femoral head osteonecrosis”. The objectives of their study were to analyze scintigraphic characteristics of the reactive interface in the early stages of AVN and to assess the prognostic value of the reactive interface in the early stages of AVN and to assess the prognostic value of the reactive interface on scintigraphy.
They concluded that the tracer uptake at the reactive interface can be different in the same stage of AVN. High tracer uptake at the reactive interface in the early phases of AVN seems to be a bad prognostic sign for femoral head collapse. In our series, Bone scan was used to see the disease progression and effectiveness of Muscle pedicle bone graft. A H/V ratio on third phase (skeletal image) is taken pre operatively and compared with post operative H/V ratio at 6 month .In our series we have found that when pre and post H/V ratio had markedly increased (greater than 1.2) then the disease was in progression stage and the procedure was not successful . When the H/V ratio was normal, decreased or slightly increased then disease was in static phase or the pathology of the disease had been halted.
In our series on comparing bone scan, among 25 hips, 5 hips showed marked increase in H/V ratio thereby showing development of secondary arthritis. 19 hips showed either normal or slight increase in the ratio or 2 hips showed slight decrease in the H/V ratio.
A statistical correlation was made using Paired T test, the P value calculated was 0.014 thereby showing statistically significant outcome of the procedure.
The main limitation of this analysis was that the sample size was small and it was difficult to decide exact cut off point at which we could say about progression of the disease. We are continuously adding more patients to get exact cut off value.
FINAL RESULTS
Above results shows that Muscle pedicle bone graft is a good option in cases of AVN. Pain is almost relieved in every case of AVN irrespective of the stage at which it is performed. However the results in terms of arrest of disease progression are much better if done in pre collapse stage. Earlier physiotherapy has a valuable role in early regaining of full range of motion.
Reference :
- Alavi A, McCloskeyJR. SteinbergME: Early detection of avascular necrosis of the femoral head by 99m technetium disphosphonate bone scans. Clin Orthop 127:137-141, 1977
Arlet J. Nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head: past, present, and future. Clin Orthop. 1994;298:191–198
- B. David Collier, Guillermo F. Carrera, Roger P. Detection of Femoral Head Avascular necrosis in Adults by SPECT J Nucl Med 26:979-987, 1985
Baksi DP: Treatment of AVN of the femoral head by drilling and muscles – pedicle bone grafting. JBJS (Br) 1991; 73(2): 241-5.
- Hull A, Hattner RS, VincenteF: Prospective scintigraphic evaluation of avascular necrosis (AVN) of the femoral head in renal transplant recipients. J Nuci Med 20:646,1979(abstr)
- Irena Seojina,Vladimir jevtic,Metka Milcinski –Bone scintigraphy as a prognostic indicator for bone collapse in the early phases of femoral head osteonecrosis.Ann Nucl Med( 2007) 21 :167-173
- Kaku Igaku. Nontraumatic femoral head necrosis: classification of bone scintigraphic findings and diagnostic value of SPECT following planar imaging 1994 Sep;31(9):1085-92
- Kim KY, Lee SH, Moon DH, Nah HY.The diagnostic value of triple head single photon emission computed tomography (3H-SPECT) in avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Int Orthop.1993;17(3):132-8.
M.Naito, K.Ogata. Quantitative bone scanning of the hip. Springer 23 oct.1996
- Miki T and Yamamuro T : Scintigraphy in Non traumatic femoral head osteoncrosis.Ann Nucl med(2005) 18:167-173
- Meyers MH: Osteonecrosis of femoral head treated with muscle pedicle bone graft. Orthopaedic Clinics of North America 1985 Oct.; 16 (4): 741-5.
- Rye Js, KIM JS. Bone SPECT is more sensitive than MRI in the detection of early osteonecrosis of the femoral head after renal transplantation. J Nucl med. 2002Aug;43(8):1006-11
|









